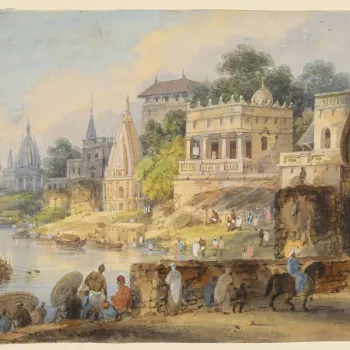The Georgians and India
Following the East India Company’s take-over of Bengal in 1765, the Company gained a greater stronghold in south India as well, centred in Madras (modern Chennai). Soon a British political representative or ‘Resident’ was sent to every significant court in the subcontinent. Here they exerted considerable influence and control.
Letters and gifts, including manuscripts and paintings,were sent from many South Asian rulers toGeorge III and George IV. East India Company officers also presented gifts to the British monarchs, and by the early nineteenth century the Royal Library had amassed one of the most splendid collections of South Asian paintings and manuscripts outside the subcontinent.